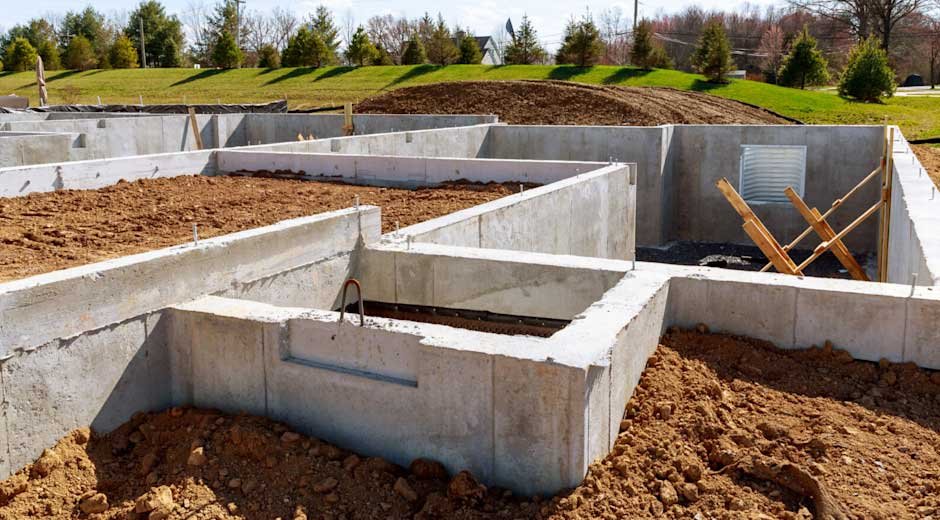
Building a home is more than just constructing walls and a roof; it begins with a strong foundation. A concrete foundation serves as the base that supports the entire structure, ensuring safety, stability, and longevity. Without careful planning and proper execution, a foundation can lead to structural issues, uneven floors, or even serious damage over time. We will explore the essential steps involved in creating a concrete foundation, focusing on methods, preparation, and materials that contribute to a durable base.
Whether constructing a residential home or a small commercial building, following these steps can save time, reduce costs, and prevent future repairs. Hiring a reliable Concrete Contractor in Milton ensures that each stage is executed correctly, from site preparation to curing. Understanding these processes enables homeowners to make informed decisions and ensures that the property remains secure for years to come. A solid foundation is not just an investment in construction but in peace of mind.
Key Steps for Building a Concrete Foundation
- Site Preparation and Soil Evaluation
Before any concrete is poured, it is crucial to prepare the site properly. This includes clearing debris, vegetation, and any unstable material that could compromise the foundation. A soil evaluation helps determine the type of foundation needed and whether additional support, such as gravel or compacted fill, is required. Soil composition affects drainage, weight distribution, and resistance to settling. Excavation follows the evaluation, with trenches or pits dug according to the planned foundation design. Proper grading ensures water flows away from the structure, preventing erosion or water damage to the foundation over time. Preparing the site thoroughly sets the stage for a foundation that can withstand environmental pressures and maintain its structural integrity throughout the building’s life.
- Formwork Installation and Reinforcement
Once the site is ready, formwork is installed to shape the foundation. These temporary molds, typically made from wood or metal, define the concrete’s size and dimensions. Reinforcement materials, such as steel rebar or wire mesh, are added within the formwork to provide tensile strength and reduce the risk of cracking. Proper placement of reinforcement is critical, as it supports the foundation under load and prevents deformation over time. Attention to detail during this stage ensures that the concrete maintains its intended shape and structural integrity. Formwork must be sturdy, level, and accurately aligned with the architectural plans to ensure the foundation meets the design specifications. Reinforcement also helps distribute weight evenly, contributing to long-term durability.
- Concrete Mixing and Pouring
The quality of the concrete mix plays a significant role in the foundation’s strength. A proper blend of cement, water, sand, and aggregate ensures durability, workability, and resistance to environmental factors. For larger projects, ready-mix concrete is often used, as it is delivered directly to the site to ensure consistency. Pouring the concrete must be done carefully, layer by layer, to avoid air pockets and uneven settling. Vibrating tools or tamping rods are used to compact the concrete and remove trapped air, resulting in a dense and uniform foundation. Monitoring the pour continuously and maintaining the correct consistency are essential to prevent weak spots or cracks. The process requires both precision and patience to ensure the foundation performs reliably over time.
- Curing and Moisture Control
After pouring, concrete needs time to cure to reach its full strength. Curing involves maintaining the concrete at a suitable temperature and moisture level to allow chemical reactions to solidify and harden the material. Typically, curing lasts at least seven days, although longer periods provide added strength and resistance to cracking. Methods such as water spraying, covering with wet blankets, or using curing compounds are common. Moisture control during curing prevents the surface from drying too quickly, which could lead to shrinkage or surface cracks. Proper curing ensures the foundation achieves maximum durability, reduces the likelihood of future structural problems, and enhances resistance to environmental stressors such as frost or heavy rain.
- Inspection and Quality Assurance
Once the foundation has cured, inspections are performed to verify its strength, alignment, and overall quality. This includes checking for level surfaces, proper dimensions, and any signs of cracks or irregularities. Addressing minor issues early can prevent significant structural problems later. Quality assurance also involves reviewing reinforcement placement, concrete density, and moisture levels during the curing process. Ensuring compliance with building codes and construction standards provides confidence that the foundation will safely support the intended load. Homeowners and builders should prioritize inspections and documentation to maintain accountability and achieve a reliable foundation that forms the backbone of a secure structure.
- Waterproofing and Drainage Solutions
A concrete foundation is exposed to soil moisture, groundwater, and various weather conditions, making waterproofing a crucial aspect. Applying sealants, membranes, or coatings to the foundation walls helps protect against water penetration, thereby reducing the risk of mold, mildew, and structural damage. Proper drainage systems, including French drains or graded slopes, divert water away from the foundation. Integrating drainage with waterproofing ensures that water does not accumulate around the base, preserving the foundation’s integrity and extending its lifespan. Thoughtful planning for water management around the foundation prevents costly repairs and safeguards the home from moisture-related issues over time.
Constructing a concrete foundation requires careful attention to planning, preparation, and execution. From site evaluation and formwork installation to pouring, curing, and waterproofing, each step plays a critical role in creating a solid base for any structure. Following these steps ensures that the home remains safe, stable, and durable for years to come. By understanding the essential processes involved, homeowners can make informed decisions, avoid costly mistakes, and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with a reliable foundation. A well-constructed concrete base is not just the beginning of a building; it is an investment in strength, safety, and longevity, forming the foundation of a home that will endure through generations.